ON 10-10-2025
By Dr. Ankur Bhanushali | General & Minimal Access Surgery | Updated for 2025
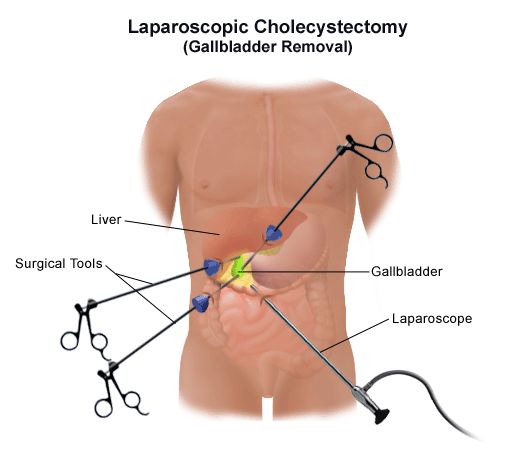
Gallbladder stones (cholelithiasis) are solid deposits that develop in the gallbladder, a small organ beneath the liver that stores bile to aid in digestion. These stones form when the balance of cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin in bile is disturbed. The stones can range in size from tiny grains to larger formations and are typically classified into two categories:
- Cholesterol Stones (most common)
- Pigment Stones (containing excess bilirubin)
While some people remain symptom-free, others may experience abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, or even infection. At Dr. Ankur Surgical Clinic, Thane, patients receive accurate diagnosis and laparoscopic solutions for gallbladder stone-related conditions.
Common Causes of Gallbladder Stones
1. Excess Cholesterol in Bile
When bile becomes oversaturated with cholesterol, it can crystallize into stones. This often results from:
- Diets high in fat and low in fiber
- Obesity or rapid weight loss
- Liver dysfunction affecting bile composition
2. Increased Bilirubin Levels
Conditions that elevate bilirubin—like liver cirrhosis, sickle cell anemia, and certain infections—can contribute to pigment stone formation.
3. Poor Gallbladder Emptying
If bile isn’t released regularly, it becomes concentrated, encouraging stone formation. Risk factors include:
- Skipping meals or fasting
- Pregnancy
- Sedentary lifestyle
4. High-Fat & High-Sugar Diet
Processed foods, sugary drinks, and fried items raise cholesterol in bile, increasing gallstone risk.
5. Obesity & Rapid Weight Loss
Both obesity and sudden weight loss (e.g., crash dieting, bariatric surgery) raise the risk of gallstones due to cholesterol fluctuations.
6. Genetic Factors
Family history can predispose individuals to gallstones due to inherited bile composition or gallbladder function.
7. Hormonal Changes
Women, especially during pregnancy, on birth control, or undergoing hormone therapy, are more prone to cholesterol-rich bile.
8. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome
High triglycerides and insulin resistance affect bile quality and promote stone formation.
9. Other Contributing Factors
- Age (more common with aging)
- Gender (more frequent in females)
- Ethnicity (notably higher among Native and Mexican Americans)
Preventive Measures
Lifestyle Changes
- Maintain a healthy BMI
- Exercise regularly
- Quit smoking and reduce alcohol consumption
Dietary Adjustments
- Emphasize whole grains, legumes, and fiber
- Avoid trans fats and processed foods
- Stay well-hydrated
- Avoid skipping meals
Medical Monitoring
- Regular health checkups
- Manage underlying conditions (e.g., diabetes, liver issues)
Conclusion
Understanding the underlying causes of gallbladder stones is the first step to prevention. Through balanced nutrition, active living, and early medical intervention, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of gallstone-related complications. For expert evaluation and laparoscopic gallbladder treatment, consult Dr. Ankur Bhanushali, a trusted name in general and minimal access surgery in Thane.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the signs of gallbladder stones?
Pain in the upper right abdomen, bloating, nausea, and intolerance to fatty food are common symptoms.
2. Can gallstones cause complications?
Yes. If untreated, they may lead to inflammation (cholecystitis), bile duct infection (cholangitis), pancreatitis, or jaundice.
3. How are gallstones diagnosed?
Typically through ultrasound, EUS (endoscopic ultrasound), or blood tests.
4. Who is more prone—men or women?
Women are more likely due to hormonal changes.
5. Do gallstones always cause pain?
Not always. Some are asymptomatic and found incidentally.
6. When is surgery needed?
Stones larger than 10 mm or causing recurrent symptoms may require laparoscopic gallbladder removal.
